|
Quiz Ja-1301 |
Match the British legislation and the correct description.
Write the correct letter to the left of the description.
|
A. Coercive Acts (or Intolerable Acts) and B. Stamp Act and Declaratory Act C. Sugar Act (or Molasses Act) and Stamp Act D. Townshend Duties (or Townshend Revenue Acts)
and Tea Act |
|
B |
1. |
These two British laws reflect the British
misunderstanding of the colonists. The first law was a tax demanding a seal
on all documents, a tax the British later rescinded in response to colonial
boycotts. The second law was a statement by the British Parliament that it
was sovereign (that it had the right to legislate for the colonies “in all
cases whatsoever”). |
|
D |
2. |
The first of these two British laws was an
attempt to get around the colonial rejection of taxes collected within the
colonies by collecting taxes at the port for commonly used imports. The
second law dealt with one of these imports, was meant to save a financially
vulnerable private British company, reduced the price of that import, and
angered colonial merchants. |
|
A |
3. |
These two British laws reveal the widening gap
between the British and the colonists. The first law was the British attempt
to force Massachusetts and Boston to back down following the Boston Tea Party
by such measures as calling for the quartering of troops by the colonists,
reducing the powers of self-government in Massachusetts, and called for royal
officers accused of crimes to be tried in Britain. The second law extended
Canadian boundaries into the |
Match the location and the description. Write the correct
letter to the left of the description.
|
A. B. Philadelphia C. Saratoga D. E. Yorktown |
|
C |
4. |
The American victory that brought about the French
alliance occurred at this location. |
|
E |
5. |
In the American south, the battle at this
location involved the French fleet, combined the French army and American
army, and resulted in the Patriots' successful end of the war for
independence. |
|
A |
6. |
The result of the War of 1812 was no real change from the
way things were before the war; however, it did result in the |
Match location and the description. Write the correct
letter to the left of the description.
|
A.
England (later called B.
France C.
Portugal D. E.
the |
|
D |
7. |
At the end of the 1400s, which European country had the most powerful monarchy and seemed to be the most powerful nation? The papacy echoed this nation’s superiority with such actions as the Line of Demarcation (Treaty of Tordesillas) dividing the new world between it and another Catholic nation. |
|
C |
8. |
What western European country was the preeminent maritime
power in the 1400s? The nation's exploration in the late 1400s concentrated on
finding a route to the Orient by sailing
east (around |
|
B |
9. |
The focus in |
|
A |
10. |
Henry
VIII of this country broke with the Roman Catholic Church because he desired an
annulment from his Catholic, Spanish queen so that he could marry again. |
|
Quiz Jb-1301 |
Match the person and the description. Write the correct
letter to the left of the description.
|
A.
John Quincy B.
Susan B. Anthony C.
John Brown D.
Frederick Douglass E.
William Lloyd Garrison F.
George I G.
George II H.
George III I. J.
Alexander Hamilton K.
Henry VIII L.
Rutherford B. Hayes M.
Anne Hutchinson |
N.
Andrew Jackson O.
John Jay P.
Thomas Jefferson Q.
Andrew Johnson R. Abraham
Lincoln S.
James Madison T.
Tom Paine U.
William Penn V.
Dred Scott W.
Elizabeth Cady X.
Harriet Beecher Stowe Y.
John Winthrop |
|
L |
1. |
This Republican
candidate in 1876 had fewer votes than the Democratic candidate, and there were
disputes over electoral ballots in four states. In return for the Democrats
accepting his victory in the Compromise of 1877, he and Republican Party
ended Reconstruction. |
|
P |
2. |
The first Secretary
of State for the |
|
S |
3. |
Sometimes
called the “Father of the Constitution,” this individual was one of the
authors of the Federalist Papers, a set of publications explaining the
Constitution and the principles behind the organization of the new
government.: |
|
D |
4. |
This
person was the leading black abolitionist. He was born into slavery, ran
away, and later bought his own freedom. He spent years lecturing in |
|
X |
5. |
The book Uncle Tom's
Cabin was
both an indicator and a cause of the growing division between North and South.
It sold over 300,000 copies in 1852, its first year, and spread the message
of abolitionism to an enormous new audience. Its author was: |
|
Q |
6. |
What former Democrat
from |
|
H |
7. |
This individual was
the King of Great Britain at the time of the American Revolution. As a |
|
M |
8. |
This
colonist offended the powers of Massachusetts Bay Colony in varied ways and
was deported from the colony. This colonist challenged the prevailing Puritan
assumptions of the proper role of women in society, argued many clergy were
not among the "elect" and had no spiritual authority, and was judged
guilty of both heresy and sedition. |
|
N |
9. |
This looser in the
election of 1824, an election he and his followers considered a “corrupt
bargain,” was able to win the Presidency in 1828. |
|
V |
10. |
The Supreme Court found
in 1857 that this individual could not bring suit to prove he was a free
person because he was not a citizen of the |
|
Quiz Jc-1301 |
Find the letter (A, B, C, D, or E on the map where the
described event happened. Then write that letter to the left of the description
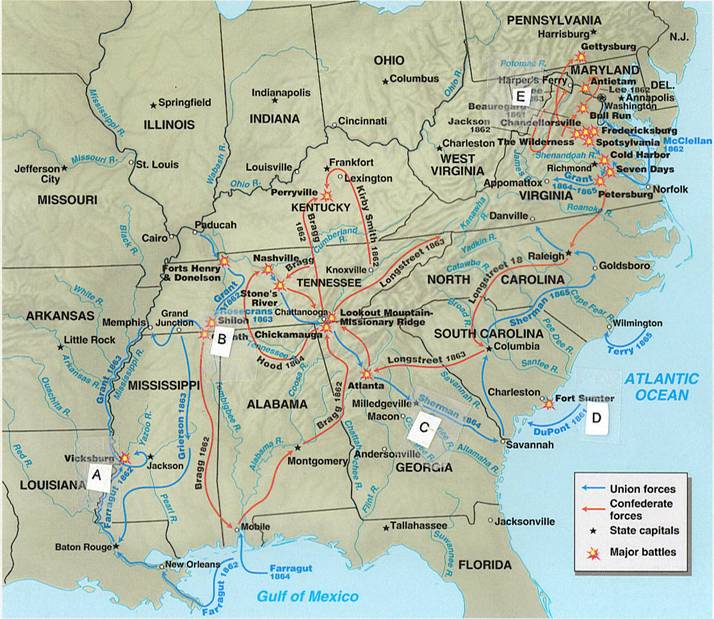
|
C |
1. |
This
engagement brought the war to the civilian population in the South and
divided the South into small portions, with the victory also uniting the
Republican Party behind |
|
a |
2. |
In
1863 two battles occurred that moved the |
|
b |
3. |
The
Western campaign was crucial to victory for the : |
|
e |
4. |
John
Brown, when in : |
|
d |
5. |
Following
this engagement in April 1861, four more slave states left the |
\
|
Quiz Jc-1301
Continued |
Match the country and the description. Write the correct
letter to the left of the description.
|
A. B.
France C. D. F. Spain |
|
|
|
E |
6. |
The
war with this nation resulted in the |
|
D |
7. |
The
|
|
B |
8. |
Because
of our treaty commitments from the American Revolutionary War and because of
our demand for rights of a neutral nation during a prolonged war, the new
nation faced repeated problems with this nation throughout the early
years. |
|
A |
9. |
This struggle occurred with states that had made demands for payment for safe passage, payments that European nations had made. The Democratic-Republican administration of President Jefferson was successful in dealing with them during the war from 1801 to 1805. This was the result of the American naval blockade of those nations, the burning of a ship, and the rescue of hostages. |
|
C |
10. |
The war of 1812 was fought with this country. |
|
Quiz Jd-1301 |
Find the letter (A, B, C, D, or E on the map where the
described event happened. Then write that letter to the left of the description
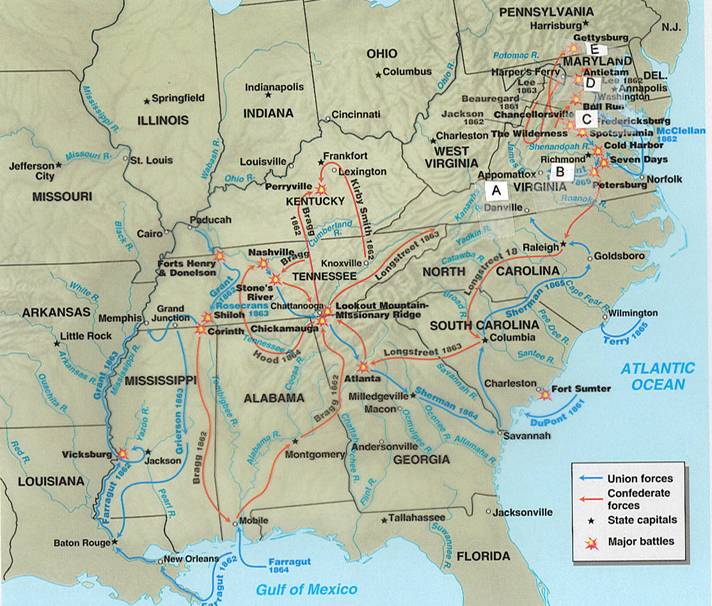
|
E |
1. |
In
1863 two battles occurred that moved the |
|
D |
2. |
This 1862 battle was among the
bloodiest engagements, it was indecisive militarily, and the North lost an
opportunity to destroy much of the Confederacy. It was, however, technically
a Union victory. President Lincoln, therefore, used the technical victory as
a justification for issuing the Emancipation Proclamation. |
|
A |
3. |
The
surrender of Robert E. Lee's worn-down forces occurred here. The surrender
took place before |
|
B |
4. |
This
city in this state was the location of the capital of the Confederacy. |
|
C |
5. |
In
July 1861, this battle, the first major battle of the war, was a Confederate
victory close to Washington, DC. Spectators came to observe the expected
Union victory, but instead they became part of a disorderly retreat. |
|
Quiz Jd-1301 Continued |
Match the item to its description.
|
A.
Emancipation Proclamation B.
Freedman’s Bureau C.
13th Amendment D.
14th Amendment E.
15th Amendment |
|
C |
6. |
This
measure, ratified in 1865, meant that slavery was no longer legal in the US. |
|
B |
7. |
This
method was the Radical Republicans' way to help the blacks and later was one
of the methods to deal with the South's actions, such as passage of black codes.
It provided food relief to poor blacks (and whites), established schools,
provided legal help, and helped some blacks find work or land. |
|
A |
8. |
With
this document in 1862, Lincoln freed the slaves in the rebellious territories.
(In other words, he freed no one.) With this document, however, he regained
control of the political competition of abolitionists in Congress, in the
military, and in the popular press while not giving the border slaveholding
states a reason to leave the Union and further provided sympathy for the
Union in England (particularly among the lower class and the middle class)
and France. This document is: |
|
D |
9. |
This measure, ratified in 1868,
was a response to the new state legislatures in the South passing black
codes. The measure defined citizenship as being born in the US or naturalized
in it, and forbade states from denying "due process" to citizens.
It also required Congressional approval for amnesty for those who had taken
an oath to support the Constitution and then violated it. It further forbade
payment of debts related to the rebellion: |
|
E |
10. |
This
measure stated that federal and state governments could not abridge the right
of a citizen to vote on account of race, color, or previous condition of
servitude. (In other words, voting could not be denied to ex-slaves.) |
|
QuizJe-1301 |
Match the term and the description. Write the correct letter
to the left of the description.
|
A. Articles of Confederation B.
Confederacy C.
Constitution D.
Declaration of Independence E.
Enlightenment F.
Impressment G.
Great Awakening H.
Manifest destiny I.
Monarchy J.
Popular sovereignty K. Protestant
Reformation L.
Reconstruction M.
Republic |
|
|
F |
1. |
During the French
and Indian War, the British had seized supposed British sailors from colonial
ports or merchant ships for service on British ships. The British resumed this
practice during its wars with France and seized supposed British sailors from
United States merchant ships, a practice that was one of the issues leading
to the War of 1812. This practice is called by what term? |
|
E |
2. |
Sir Isaac Newton and
John Locke challenged traditional notions that humans had no role in
determining their fate and were part of a movement known as the
_____________________. |
|
L |
3. |
The period following
the Civil War until the Compromise of 1877 is called by what term? |
|
G |
4. |
The
movement leading to waves of religious revivals beginning in the 1730s and
spreading throughout the English colonies was _____. |
|
M |
5. |
This
word was central to citizens in the late 1700s. The BEST definition of the word is a government without monarchy or
aristocracy, one with the power in the hands of the citizens who vote for
representatives. |
|
D |
6. |
The ______________
expressed these "self-evident truths" previously expressed by Enlightenment
authors: - "All men are created equal." - The
"Creator" endows them with "unalienable rights,"
including "life" and "liberty." - The reason for the
existence of government is to "secure these rights"--rights that
were given by the Creator and not by the government. - If a government
does not secure these rights, the contract between the people and the
government is broken and the people have a right and duty to replace it. |
|
B |
7. |
The
new Constitution of the seceding South prohibited protective tariffs,
guaranteed slavery, and protected slavery in any new territories, and
protected the dominance of sovereign states over a central government. The
form of government and the key word in its name for its new nation was this
term. |
|
H |
8. |
The
term ________________________ can be defined as the view that the United
States was justified by God and history to expand its land. This movement
became national policy with the election of President Polk in 1844 and his
campaign for acquisition of both Oregon and Texas. |
|
J |
9. |
The
political position that the people should, by their votes, be the ones to
decide on the matter of slavery in the territories was called
___________________________. This position became a national issue because of
expansion into the Kansas-Nebraska territories. |
|
K |
10. |
Martin Luther and
John Calvin advocated ideas of religious reform of the Roman Catholic Church
and influenced many groups including the Puritans. They are both associated with
this movement in the 1500s. |
|
Quiz Jf-1301 |
Find the letter (A, B, C, D, or E) on the map where the
described event happened. With rivers, the letter is placed immediately below the blue box marking the river.
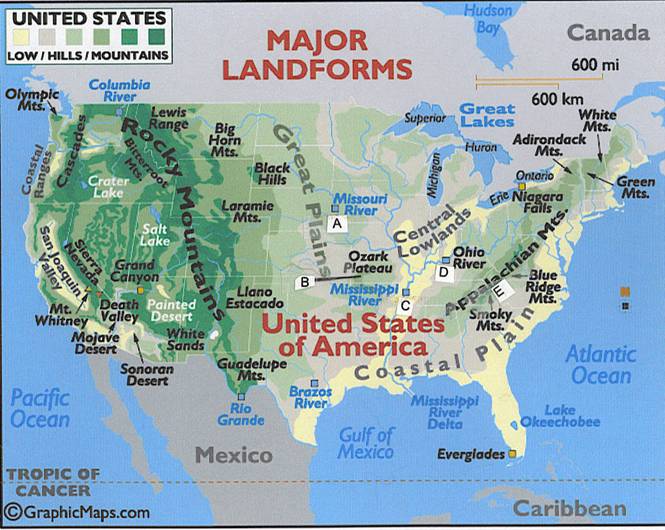
|
D |
1. |
The French and Indian War included a battle at
Fort Duquesne, an area where two rivers merged to create the ____ River. The
battle represented some of the assumptions, alliances, and goals of the war
itself: - British generals were concerned about their ability
to defeat the French and the Native Americans in a frontier war. - Native Americans, such as the Algonquians,
supported the French as a way to drive out the British colonists. - Virginia colonists, including George Washington,
were involved because the colony’s charter included the land in this fertile
valley. |
|
E |
2. |
This area was the
barrier following the end of the French and Indian War (the Seven Years War)
with the Proclamation Line of 1763. |
|
C |
3. |
This area was the
barrier at the end of the American Revolution. It was the boundary set by the
British at the peace treaty. |
|
A |
4. |
The era before 1776 and after focused on the new lands for settlement in one fertile river valley. Another famous river opened up the newly purchased Louisiana Territory to the exploration of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. This river was__________. |
|
B |
5. |
Among the decisions on slavery in the early 1800s was the _________ Compromise. With the exception of this state, this 1820 legislation prohibited slavery north of the 36 30' parallel, the lower boundary of the state. (It also used admission of an equal number of slave and free states as the solution to the nation's sectional divisions.) |
Quiz Jf-1301
Continued |
Use the letter A,
B, or C for the colonial region where the described event happened. You may use the letters more than once.
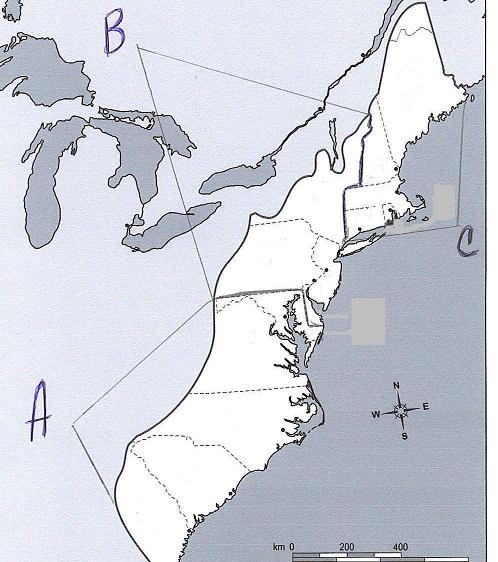
|
C |
6. |
This colonial region
included a colony requiring towns to financially support basic education. The
region developed the colleges of Harvard and, later, Yale to educate
clergymen, with Yale being formed by conservatives concerned about the
religious liberalism of Harvard. |
|
A |
7. |
This colonial region
is predominantly associated with the Anglican religion, but is later
influenced by religions such as Methodism. |
|
B |
8. |
This colonial region
is predominantly associated with diverse religions, with diverse agriculture
and trades, with export of wheat, and with having the largest ports in the
colonies (as well as other cities). |
|
C |
9. |
In the town of Salem
in this region, charges of witchcraft caused considerable turmoil in the late
1600s and reflected the disruptions in the region. |
|
A |
10. |
This colonial region also exported wood and naval stores
(products used when building or maintaining wooden ships), but it is
predominantly associated with export of commercial crops that relied on slave
labor (crops of tobacco and rice in the colonial era and of cotton later).
One of the colonies in this region was the location of Bacon’s Rebellion in
the late 1600s, a rebellion reflecting the disruptions in the region. |